The definition of maintenance operations is not limited to simple interventions on faulty equipment. It encompasses a range of essential activities aimed at ensuring the functional continuity and safety of facilities. This approach includes repair, preventive, and corrective processes, which can vary depending on the industrial context. Beyond technical aspects, good management of maintenance operations also contributes to cost optimization and maximizing the performance of equipment, which is crucial in many industries.
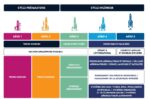
Maintenance operations are a set of essential activities designed to ensure the availability and performance of systems, machines, and equipment within a company. They primarily fall into three main categories: maintenance, repair, and operations. Each of these steps plays a crucial role in the continuity of production and in the safety of industrial operations.
Maintenance, in a broad sense, is the action of preserving and keeping equipment in good working condition. It includes preventive practices that aim to anticipate breakdowns before they occur. This can include measures such as regular cleaning, technical checks, and the replacement of parts likely to wear out over time. The goal of preventive maintenance is to intervene before a malfunction manifests, thereby minimizing machine downtime.
Repair, on the other hand, comes into play when systems fail. It is a corrective response aimed at getting the equipment back in working order. This type of operation is often more expensive and requires quick technical interventions to avoid prolonged interruptions of activities. Repair operations generally require a detailed analysis of the causes of the failure, in order to avoid repeating the same mistakes in the future.
Operations refer to the set of maintenance and repair activities implemented within an organizational framework. This includes planning interventions, developing maintenance schedules, managing spare parts inventory, and monitoring equipment performance. Proper organization of operations is therefore fundamental in ensuring the proper functioning and durability of facilities.
Other essential elements relate to maintenance management. For example, using predictive maintenance tools allows for analyzing potential problems using real-time data and advanced algorithms. This enables a proactive and more targeted approach, thereby reducing costs and improving efficiency. Companies must also train their staff on these tools to maximize their impact.
Another inseparable aspect of maintenance operations is documentation. Every intervention, whether it is preventive maintenance or a repair, must be subject to strict traceability. This not only helps measure the effectiveness of operations but also ensures the safety of employees by providing them with accurate data on past interventions and the real-time status of equipment.
It is also important to note that organizational culture plays a significant role in the implementation of effective maintenance operations. An engaged management that values maintenance as a key function of the company contributes to motivating staff to take their responsibilities seriously, thus reducing the risk of neglect and accidents.
In conclusion, understanding the definition of maintenance operations is fundamental for any organization seeking to improve its performance levels. This involves considering not only the technical aspects but also the human and organizational elements that interact to ensure optimal functioning of machines and systems. Companies that invest in effective maintenance operations can expect significant improvements in their productivity and profitability in the long term.

FAQ on Maintenance Operations
Q : What is maintenance?
A : Maintenance refers to a set of processes and practices aimed at ensuring the continuous and effective operation of machines, equipment, and other assets in a company.
Q : What are the main objectives of maintenance?
A : The main objectives of maintenance are to ensure the availability, performance, and safety of equipment while minimizing service interruptions.
Q : What are the different types of maintenance?
A : The two main types of maintenance are corrective maintenance, which occurs after a failure, and preventive maintenance, which aims to anticipate breakdowns before they occur.
Q : How does a maintenance process generally unfold?
A : A maintenance process often begins with an assessment of the equipment’s condition, followed by planning the necessary interventions, then executing repairs, and finally conducting checks to ensure proper functioning.
Q : What activities are included in maintenance?
A : Maintenance includes activities such as repair, monitoring, inspection, cleaning, and adjustment of machines and equipment.
Q : Why is it important to integrate an appropriate maintenance strategy?
A : Integrating an appropriate maintenance strategy is crucial to prolonging the lifespan of equipment, reducing operating costs, and improving workplace safety.
Q : How can data collection assist in the maintenance process?
A : Data collection allows for analyzing the performance of equipment, thus enabling the anticipation of failures and optimizing maintenance interventions.