In the fascinating landscape of astronautics, Gus Grissom stands out as an iconic figure whose exploits marked the beginnings of American space exploration. As a pioneer of Mercury program, he became the second American to launch into space, participating in the mission that paved the way for the conquest of Earth’s orbit. Subsequently, as commander of Gemini program, Grissom played a key role in developing new techniques that laid the foundation for the Apollo missions. His audacity and determination not only shaped his personal journey, but also left an indelible mark on the history of astronautics.
Table des matières
ToggleGus Grissom’s Legacy in Astronautics
Virgil “Gus” Grissom is undoubtedly one of the emblematic figures in the history of astronautics. His journey begins with the Mercury program, where he plays a key role as the second American to travel to space. By carrying out the flight Mercury-Redstone 4 In 1961, Grissom paved the way for human exploration of space, thus testifying to American audacity in the space race.
But it is with the Gemini program that Gus Grissom makes an even bigger impact. As commander of the Gemini 3 mission, he experiences a crucial innovation while flying with a crew of two astronauts. This constitutes a significant step towards preparing for more complex missions to come, notably the Apollo program.
His determined character, combined with his avant-garde vision, made it possible to strengthen the foundations of the conquest of space. Grissom thus became a symbol not only of bravery, but also of an era where man looked to the heavens with the hope of realizing his wildest dreams.

Gus Grissom: Pioneer of Astronautics
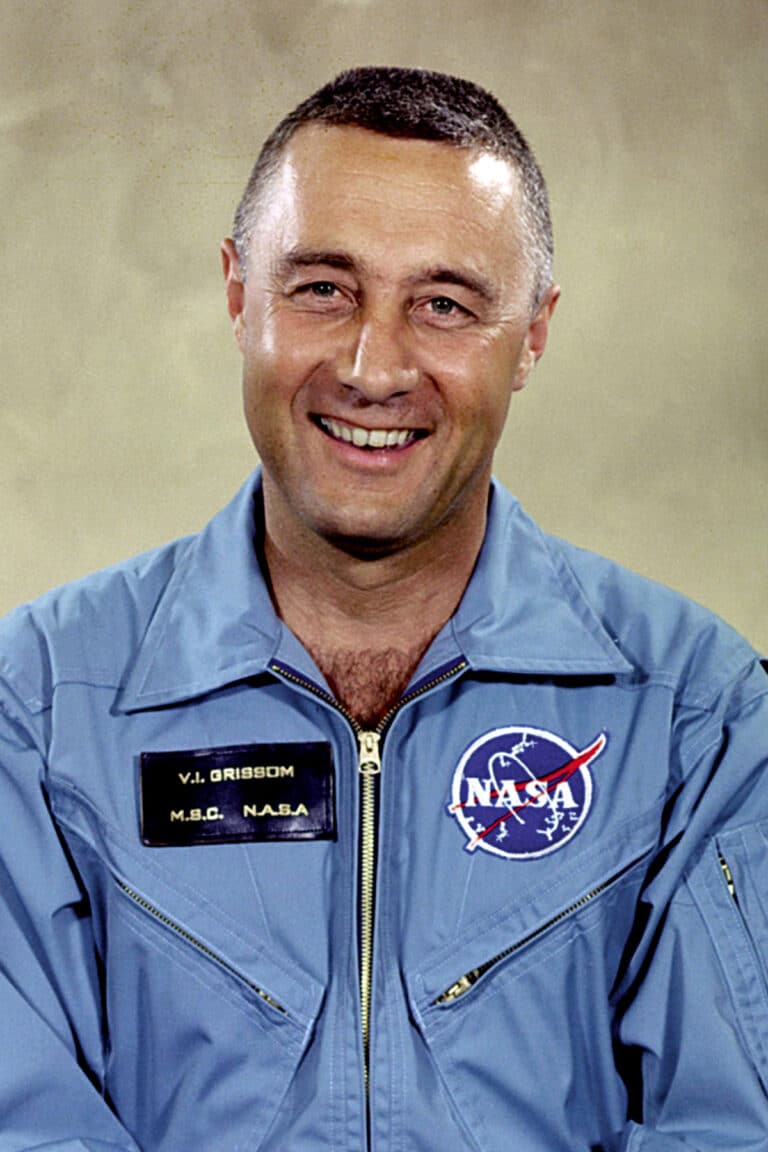
Virgil Ivan Grissom, commonly known as Gus Grissom, is an emblematic figure in the history of astronautics. Born in 1926, he distinguished himself by becoming one of the first American astronauts, playing an essential role in the programs Mercury And Gemini. His journey is punctuated with challenges, innovations and an unwavering determination that have contributed to the advancement of space exploration.
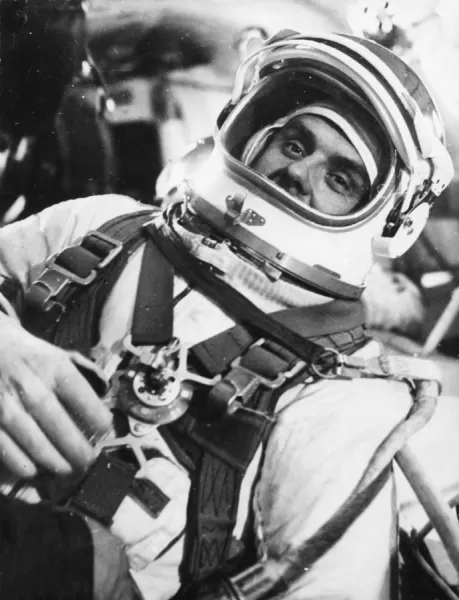
The program Mercury, launched in 1958 by NASA, aimed to send the first Americans into space. Grissom joins this adventure as a member of the first group of selected astronauts. In 1961, he made his first space flight aboard Mercury-Redstone 4, becoming the second American to travel into space after Alan Shepard. This 15-minute flight was a significant breakthrough, not only for Grissom, but for all of humanity, demonstrating America’s capabilities in space exploration.
This journey, however, is not without incident. Following his theft, Grissom finds himself in a delicate situation. He expresses his frustration at the breakdown of his ship which, upon his return, required additional protection. This experience begins a dialogue about the risks associated with space and the improvements needed to ensure the safety of astronauts.
Grissom doesn’t stop there. In 1965, he assumed the position of commander for the program Gemini. This series of missions allowed the United States to test new orbit techniques, including orbital rendezvous and spacewalks. On this occasion, Grissom and his partner, John Young, carried out maneuvers which foreshadowed future lunar missions. His leadership and crisis management skills during this mission were praised by his peers and NASA leaders.
Unfortunately, Grissom sees his career take a tragic turn with the mission Apollo 1. In January 1967, the spacecraft suffered a fire during a ground test, resulting in the deaths of Grissom and his crewmates. This devastating event sent shock waves through the world of aeronautics. Their lost lives not only marked a turning point in NASA history, but also spawned fundamental reforms in spacecraft safety. Grissom’s work and ultimate sacrifice helped shine a light on the importance of safety in future space missions.
Despite his tragic end, Gus Grissom’s legacy endures. As a pioneer, he paved the way for generations of astronauts. His spirit of innovation, his courage and his commitment to space exploration made him a legend in the field of astronautics. The discoveries and lessons learned from his experiments continue to influence the trajectory of NASA and space missions around the world. Grissom is and will remain one of the heroes of our conquest of space.